Introduction
Stigum (2021) said that there is a relation between the choices of the consumer and the demand curve. The graphical representation of this relationship is done in accordance with the microeconomics where the choice of the consumers to spend money is related to the demand curve of consumers is given by the theory of consumer choice. This theory evaluates the desirability of a consumer to consume a good and the restriction of the consumer to spend on it. The focus of this theory is to elevate the utility according to the budget constraints of customers.
In other words, it can be said that this theory revolves around analyzing the choice of the consumer and analyzing the factors that cause an impact on the consumer’s preference. The demand for goods is related to the preferences of consumers and this is why this theory affects the demand curve as well (André et al., 2018). Logically, if the choice of the consumers is in the favor of a good, and also the factors affecting the choice of the consumers are in the favor of the good, then the demand of the product elevates. This causes a rightward shift in the demand curve. Where if the choice of the consumers is not inclined towards the product and even the factors impacting the preferences of the are not favorable for the product. Then, the demand for the product declines, which causes a leftward shift in the demand curve.
Biondi et al. (2019) discussed that consumption of a product by a consumer is derived from two types of situations, the first is where the consumer has a huge level of interest in the products, and thus, the consumption of the product shall be availing a huge amount of satisfaction or pleasure to the customers. Here, the consumer is derived from the interest of the consumers. Another situation is the consumers have no interest in the product, however, the other motivational factor inspires the consumers to make a choice to consumers the product. It can be evaluated that in the two situations, the first one depicts the consumption of the product is induced by the direct choice of the consumers. Whereas in the second situation, the consumption is induced by indirect choice. Summing up, it can be said that the choice of the consumer is that aspect which makes the consumers buy the products. Thus, the factors affecting the choice of the consumers are vital to be read to understand the direction of the customer’s choice.
André et al. (2018) said that the production and consumption of a product are related to each other. However, here also the factors of the preferences of the consumer play a vital role. If the consumer’s choice is favorable for the products, the demands of the product rise in the markets. This gives an opportunity to the producer to earn for the sales of that product. This is how the product gets included by the consumer’s choice. It has to be seen that due to the favorable consumer choices the price and availability of the product get affected. The cycle is not over yet, due to the alteration the preferences of the consumers are again affected, which affects the product’s demand in the market.
According to assignment help experts s the choices of the consumer are for maximizing his or her utility. Utility is an economic term describing the sense of satisfaction or pleasure. A choice of a consumer towards any product describes the level of his utility to that product. It can be understood by an example: a person who is fond of perfume, his or her utility after buying a performance shall be high. On the other hand, for a person who is not much fond of perfumes, his or her utility after buying a perfume shall not be much higher. This is the rate of satisfaction one receives from a product as per his or her choice. The above paragraph is enough to understand that the ultimate aim of a customer for making the choices and then purchasing the product is to gain satisfaction from the product. This also means the intention is to maximize his or her utility from the product.
Indifference Curve
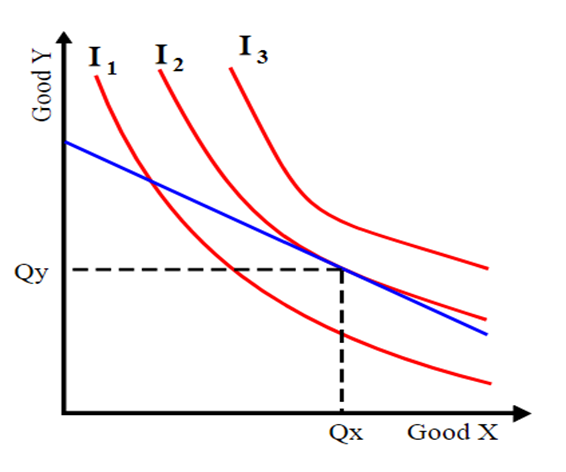
Roldán et al. (2022) said that the indifference curve is an excellent example to represent the maximization of the consumer’s utility by the consumption of more than one product. Here, more than one product is considered, because a person is surely not going to spend all his or her income on the purchase of only one product. The person is surely going to buy multiple products for the fulfillment of his or her needs. An indifference curve is a graphical representation that visualizes the combination of two kinds of products that provide equalized utility to the consumers. There are several points on the graph which represent the indifference of the numbers for both the products, however, the utility derived from each one of them is equal.
In the case of maximizing the utility, the consumer focuses on two products with two kinds of prices and the expenditure of the consumer on each of them happens differently due to this difference in the prices. This is where it signifies that for maximizing the utility, the consumer’s marginal rate of substitution is equivalent to the ratios of the two product’s prices. These terms “Consumer’s marginal rate of substitute” are used to denote the substitution of another product that is done by a customer to purchase the other product and finally balance out the utility (Ozenbas et al., 2022).
(Source: Roldán et al., 2022)
In this indifference curve, good X and Good Y are taken and Qy is the quantity of the good Y that has to be purchased by the consumers and Qx is the quality of Good X which has to be purchased by the customers in order to maximize the utility and meet the balance point of intersection given on the budget line (represented as blue). To know more about this Indifference Curve students can take help from SourceEssay economics assignment help experts .
Factors Affecting The Theory Of Consumer Choice
Factors associated with the purchasing power of the consumers affect the choices of the consumer. This is why these are the factors that affect the demand as well as sales of the product in the market. There are three factors that affect the choices of the consumers and thus, the consumption of the product. These factors are income, price, and substitute products.
(Source: Jing et al., 2019)
Income– The income of the consumers is the key aspect that decides her buying power. Every human has a fixed budget and even people can be categorized as per their affordability according to their budget. This is why the budget is a huge factor impacting the consumer’s choice (Jing et al., 2019).
Price– The price of the product also affects the preferences of the consumers to buy it. The higher price creates pressure on the people with limited budgets whereas the lesser prices of the product create a positive effect on such consumers.
Substitute:- There are always multiple products of the same category in the market. This creates a scenario where a consumer gets a lot of options for the selection of a single kind of product. Thus, the substitute product surely influences the choice of the consumer.
Wai et al. (2019) noted that the presence of another product in the maker can attract the attention of the consumers and make the consumer purchase it. However, this logic is not that simple, even this inclination of the consumer’s choice towards a particular product is based on the multiple factors affecting the consumer’s preferences. The factors that impact the consumer’s choices change the statistics based on which the product is being projected into the market and also the way consumers perceive the product.
These three factors affecting the choices of the customers and their effects are known as substitute effects, effect of purchasing power, and income effect. All of them alter the consumer’s choices in both positive as well as negative ways depending on the statistic of the effect.
Effects Due To The Factors On Consumer’s Choice
Income Effect– The impact of income on the consumers on his or her choices is huge. This is because due to the state of the income, a consumer decides the best choices of his or her fulfillment of needs. The income effect is applicable for both positive and negative effects on the demands of a product by altering the consumer’s choices. Keeping the price of the product the same, if the income of the consumer improves, the restriction due to budget gets decreased which gives the person a chance to purchase the product (if the price of the product fits into the budget). Thus, here the income of the consumer affected the demands of the product positively by affecting the choice of the consumers positively. However, in a case where the price of the product is constant, but the income of the consumers decreases, and thus, the product’s price is not being fit into the consumer’s budget (Dargahi et al., 2020). Here, the income affected the choice of the customer negatively. This results in a negative effect on product demand.
Purchasing Power– Purchasing power is the capability of the consumers to buy things of their preferences. First of all, the purchasing power of the consumer is affected by two factors: the income of the customers and also by the price of the product. The effect due to the income of the customer has been discussed above, the here the second aspect is the price of the product affecting the purchasing power. If the alterations happen in the price of the products and the income of the consumer is kept fixed. Any enhancement in the product’s price shall cause a restriction to the purchasing power of the consumer due to fixed income. Thus, this shall affect the consumer’s choice negatively. Similarly, the lower of the product’s price shall boost the purchasing power of the consumers, which shall affect the consumer positively.
Substitute Effect– Ikonen et al. (2020) noted that the presence of substitutes in the markets is described by the purchasing power of the customers, which is affected by the income of the customer this effect comes to play on the consumer’s choice only when the two factors mentioned above goes unfavorable for the customer’s choices for a product and make their attention deviate to the other product of the same niche. If the income of the consumer is not in favor of the purchasing power of the customers, there shall be an automatic shift in the interest of the customers to find some other product of the same niche but of a lower price. If the income of the customers enhances and strengthens the purchasing power of the customers, then the interest of the customers gets distracted towards the product of high price. Usually, for this aspect, the customer’s utility for the product changes, and then the intention of the customers shift to purchasing a product of higher price but same niche.
Significance Of The Theory Of Consumer’s Choice
Economically, the consumers are the determinants of the product that shall be produced. This happens due to the choice of the customers (Pereira et al., 2021). The choices of the customers indicated the demands of the product and this is how the producer finds opportunities and makes the products. Thus, the first and foremost significance of consumers’ choice is on the demands of the products in the market and then their availability.
For the business person, it is vital to understand the consumer’s choice as it can be understood by the above paragraph. If a product does not come in the preference list of the customers then no selling of the product shall happen. This shall impact the overall performance of the business. This is the reason that determines why it is essential in the business world, it is a vital concept to be understood, and analyzed in order to ensure the production as per the demand in the market.
Hamadneh et al. (2021) described that every operation happening in the professional world is linked with profit. Ultimately money is the key. This is what makes this theory of consumer choice readable and valuable. This theory highlights the key aspects that affect the building of the choice of consumers as well as its maintenance. When such things are recognized by the business persons, the evaluation of the demand can be done in better ways, and thus, the product of the accurate product can be done effectively. This theory also evaluates the indifference curve which provides a ground for customers to analyze in what ways the purchase of their desired goods shall be done to maximize their utility.
Criticism Of The Theory Of Consumer’s Choice
The theory has been quite effective still there is a lot of criticism on it. It is said that the theory explains more on how the consumer should act on their choice rather than focusing on the real version of how the alteration of consumer’s choices. As per the neoclassical consumer theory, it is said that this theory can be rejected if the consumer’s choice is seen by the glasses of behavioral economics. There are certain times when a consumer might make choices by neglecting the few factors listed by the theory of consumer choices. Such situations reveal the parameter on which the real-life pattern exists.
Some of the criticisms that are given for this theory of consumer’s choice is listed below:-
- A sudden rise in interest is a common thing that can happen to any human belonging. Many times, it is observed that a consumer makes a list of shopping items and visits the place but suddenly finds something that creates interest to the person and he or she buys it on the basis of that interest. Here, surely the choice of the consumers played a role but the utility function has no role because the moment the person bought the product impulsively, the balance that was formed by his or her on the shopping list got disturbed.
- In the view point of thesis help experts consumers do not make evaluating decisions every time, no exact calculation is done by them to buy the good. They just do the calculation by using their rough mathematical statistics. This is why there is no need of evaluating the indifference curve and thus, going through those calculations does not matter at all.
- This theory is not applicable for all kinds of goods because there are some goods that are bought by the consumers only on a few occasions and also in less frequency. Examples of such goods are:- car, refrigerator, etc. Moreover, such goods cannot be split and this is why the balance that has to be done in the quantity of purchase of goods for utility maximization shall not be applicable (Pettinger, 2022).
Thus, it can be said that the theory seems to be evaluating the consumer’s choices to some extent. When it comes to the key factors like the price of the product, consumers’ incomes, and availability of substitute products. The impacts of these aspects on consumer’s choice can be evaluated but there are other aspects as well; that exist in real life, which cannot be calculated. Especially the indifference curve is not applicable in most of the incidents that happen to consumers while making choices which further included their purchasing decision.
Reference List
André, Q., Carmon, Z., Wertenbroch, K., Crum, A., Frank, D., Goldstein, W., Huber, J., Van Boven, L., Weber, B. and Yang, H., 2018. Consumer choice and autonomy in the age of artificial intelligence and big data. Customer needs and solutions, 5(1), pp.28-37.
Biondi, B., Van der Lans, I.A., Mazzocchi, M., Fischer, A.R., Van Trijp, H.C. and Camanzi, L., 2019. Modelling consumer choice through the random regret minimization model: An application in the food domain. Food Quality and Preference, 73, pp.97-109.
Dargahi, R., Namin, A. and Ketron, S., 2020. Co-production or DIY: an analytical model of consumer choice and social preferences. Journal of Product & Brand Management.
Hamadneh, S., Hassan, J., Alshurideh, M., Al Kurdi, B. and Aburayya, A., 2021. The effect of brand personality on consumer self-identity: the moderation effect of cultural orientations among British and Chinese consumers. Journal of Legal, Ethical and Regulatory Issues, 24, pp.1-14.
Ikonen, I., Sotgiu, F., Aydinli, A. and Verlegh, P.W., 2020. Consumer effects of front-of-package nutrition labeling: An interdisciplinary meta-analysis. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 48(3), pp.360-383.
Jing, P., Huang, H., Ran, B., Zhan, F. and Shi, Y., 2019. Exploring the factors affecting mode choice Intention of autonomous vehicle based on an extended theory of planned behavior—A case study in China. Sustainability, 11(4), p.1155.
Ozenbas, D., Pagano, M.S., Schwartz, R.A. and Weber, B.W., 2022. Economics and the Equity Market: A Microeconomics Course Application. In Liquidity, Markets and Trading in Action (pp. 1-19). Springer, Cham.
Pereira, L., Carvalho, R., Dias, Á., Costa, R. and António, N., 2021. How does sustainability affect consumer choices in the fashion industry?. Resources, 10(4), p.38.
Pettinger, T., 2022. Consumer choice – Economics Help. [online] Economics Help. Available at: <https://www.economicshelp.org/university/consumer-choice/> [Accessed 2 March 2022].
Roldán, D., Cisneros, A.A., Roldán-Aráuz, F., Angamarca, S.L. and Zambrano, A.R., 2022. An analysis of indifference curves and areas from a human nutrition perspective. arXiv preprint arXiv:2202.13276.
Stigum, B.P., 2021. Consumer Choice under Certainty and Uncertainty in Applied Econometrics (No. EERI RP 2021/08). Economics and Econometrics Research Institute (EERI), Brussels.
Wai, K., Dastane, O., Johari, Z. and Ismail, N.B., 2019. Perceived risk factors affecting consumers’ online shopping behaviour. The Journal of Asian Finance, Economics and Business, 6(4), pp.246-260.