Introduction:
In the hyper-connected global manufacturing industry these days, both intermodal transportation and international logistics serve as the two driving forces that facilitate the movement of raw materials and final products across borders (Zelikov et al.2019). In this intricate network of international logistics, intermodal transportation continues to emerge as a critical element. However, assignment help Leeds and this blog report is going to explore the impacts of intermodal transportation and international logistics on global manufacturing businesses in ensuring effective and efficient trade worldwide (Colicchia et al.2017).
Intermodal logistics and its impact on manufacturing businesses:
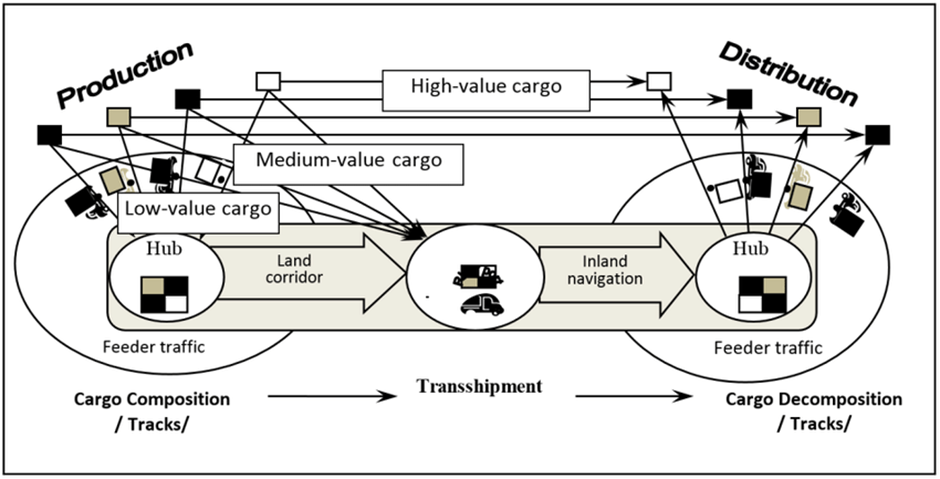
Figure 1. Intermodal transportation
(Source: Fernández et al.2022)
Intermodal logistics can be defined as the movement of products employing different transportation modes including trains, trucks, planes and ships within a single journey. It provides effective and flexible solutions as in assignment help Luton and to address the challenges related to cross-border transportation by utilising specialised containers that are capable of transitioning smoothly between various transportation modes, ensuring a seamless flow of products from the manufacturing centres to their destinations (Hayashi and NEMOTO, 2021). Intermodal logistics includes a system for the transportation of products, essentially over larger distances by using a collection of two or more transportation modes. For instance, two modes utilised in combination might include rail freight and road haulage or inland waterway barge and road haulage to accomplish the most efficient, eco-friendly and economical delivery offloads to the destinations (Kosuge et al.2024). Intermodal logistics offers manufacturing companies with flexible alternatives across their domestic and international supply chain since they transport their products from the sources to the consumers (Göçmen and Erol, 2018). This logistics remains the beginning to be embedded more frequently into the manufacturing supply chain approaches in the ever-evolving transportation industry these days allowing for optimising trade-offs among different supply chain elements and the cost and service aspects associated with transportation (Gronalt et al.2019). Intermodal allows manufacturing businesses to cut back on their shipping efforts and costs successfully for long-distance movements while adding value to the bottom line of the manufacturers by presenting potential savings as compared to conventional over-the-road trucking (Agamez-Arias and Moyano-Fuentes, 2017).
Intermodal logistics enables manufacturing companies to optimise their route planning, minimising transit duration and improving the overall efficiency of their supply chain. The capability of switching smoothly between various transportation modes ensures the fastest delivery reducing the potential for any disruptions. Additionally, by embracing different modes of transportation, intermodal logistics is capable of accomplishing cost savings across economies of scale (Fernández et al.2022). The usage of large containers, reduced requirements for storage and handling and cargo consolidation facilitate the potential cost-effectiveness of different manufacturing businesses. Furthermore, intermodal logistics present ecological benefits by eliminating the carbon footprints of the manufacturing companies to a larger extent. Employing more fuel-efficient transportation modes like ships and trains to cover larger distances allows for reducing the environmental footprint of transportation, empowering sustainable practices. Moreover, intermodal logistics offers the flexibility of adapting to dynamic manufacturing market environments as well as associated underlying disruptions (Hasan et al.2021). If any particular transportation mode encounters challenges like climate disruption or capacity limitations, the capability of switching to an alternative mode helps keep the supply chain activities uninterrupted. Notwithstanding that, intermodal logistics allows for smooth movements of products across the borders, connecting various continents and regions resulting in facilitating global trade with promoting economic development by linking manufacturers with the suppliers and consumers across the sphere (Göçmen and Erol, 2018). The domain of intermodal logistics and manufacturing has continually been emerging to fulfil the demands of the dynamic marketplace. Technological advancement including advanced data analytics and real-time monitoring and tracking keep on adding value to the control and visibility of the manufacturing supply chain worldwide whereas initiatives including blockchain technology have been enriching security and transparency in the logistics systems across the contemporary manufacturing industry (HaYasHI and NEMOTO, 2021).
The impacts of international logistics on different manufacturing companies:
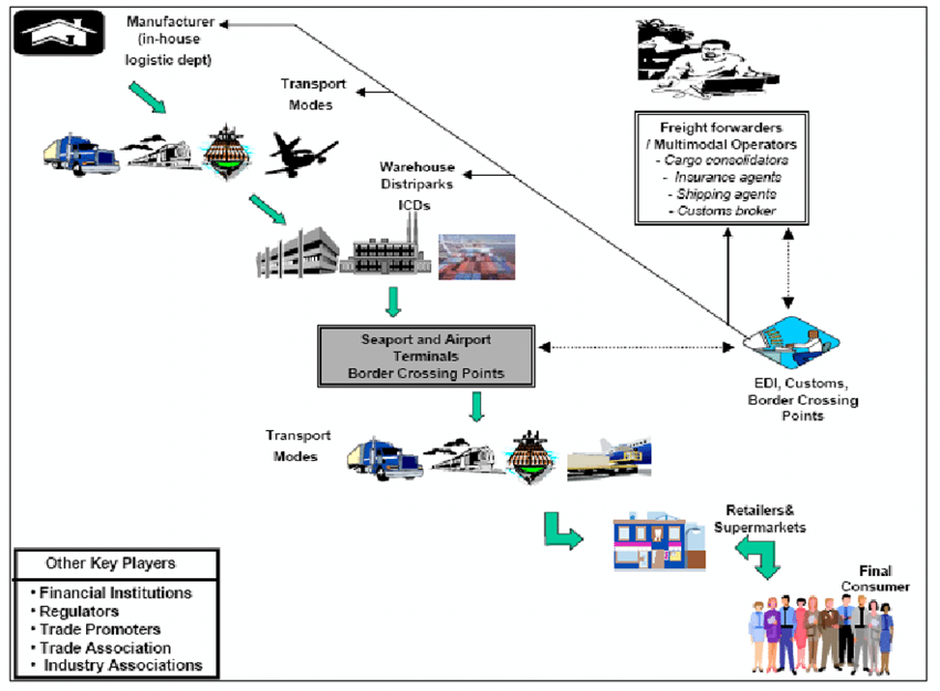
Figure 2. The impacts of international logistics on different manufacturing companies
(Source: Kosuge et al.2024)
International logistics involves planning, organization, monitoring and controlling the flow of information, resources and products across the borders. It includes the collaboration of transportation, warehousing, distribution, documentation and customs clearance to ensure the cosy-efficient and on-time product delivery to the consumers. Manufacturing businesses nowadays run in a hyper-connected international business place where products and services continue traversing borders at an unparalleled pace (Hasan et al.2021). Logistics plays a pivotal role in increasing the dynamism of the global manufacturing sector by staying the backbone of international commerce and incorporating invisible support to ensure seamless movements of products from the manufacturers to the consumers around larger distances (Shibasaki et al.2021). International logistics entails different operations from procurement and manufacturing to warehousing, transportation, distribution and delivery with looking forward to optimising the flow of information, resources, finances and products across the global manufacturing supply chain (Fernández et al.2022).
When it comes to portraying the impacts that international logistics have on different manufacturing businesses, it has been analysed that international logistics allows the manufacturers to extend their market reach and thereby tap into new markets worldwide resulting in facilitating the efficiency of product movement from manufacturing regions to global distributors, retail outlets and consumers (Kosuge et al.2024). Furthermore, international logistics enables manufacturers to optimise costs by picking up the most convenient and cost-effective routes of transportation, consolidating shipments to accomplish economies of scale as well as embracing the approaches to freight negotiation. Efficient logistics strategies are capable enough of cutting back on the transportation expenses of the manufacturers and thereby adding value to the effectiveness of their overall supply chain operations (Colicchia et al.2017). In addition to that, international logistics promotes on-time product delivery, which remains essential in order to match the expectations of the consumers while maintaining a competitive position in the industry. Effective and seamless coordination of documentation, transportation and custom clearances contributes to the reduction of lead times as well as delays in delivery (Göçmen and Erol, 2018).
Moreover, assignment help Sheffield and international logistics supports adherence to the export and import regulations, standards and legislations, risk mitigation practices and customs compliance. By maintaining compliance with the legal and regulatory necessities as well as eradicating associated risks, manufacturing businesses become capable of avoiding delays, penalties and reputational damages (Kosuge et al.2024). Additionally, international logistics accelerates supply chain visibility by developing a strong coordination between different stakeholders such as suppliers, manufacturers, transportation service providers, customers and customs authorities while this enriched supply chain visibility allows for improved collaboration, proactive dispute resolution and informed decision-making by the manufacturing companies. Be that as it may, international logistics helps in effective tracking and communication, allowing the consumers to maintain an eye on their shipments, get updates about their orders and plan accordingly resulting in increasing transparency between manufacturers and their global consumers while building confidence and reducing disruptions across the global manufacturing supply chains (Göçmen and Erol, 2018). Furthermore, international logistics is capable of catering to particular demands of the consumers including eco-friendly options and expedited shipping, elevating further their satisfaction levels finally a well-structured global logistics framework becomes capable of meeting and exceeding the expectations and requirements of the consumers, adding value to their overall purchasing experience and cultivating enduring trade relationships in the dynamic global manufacturing industry environment (Hasan et al.2021). Then again, international logistics plays a crucial role in increasing the market expansion across the international industry for the manufacturers. With effective and seamless logistics processes in place, different manufacturing businesses accomplish the capability of penetrating rapidly new markets and thereby capitalising on emerging market opportunities across the globe (Fernández et al.2022).
By leveraging supply chain processes and transportation networks, international logistics cuts back on lead times, allowing the manufacturers to get their global consumers faster. This speed to the market is considered a competitive benefit for the manufacturers essentially in such an industry where time to the market remains crucial for the businesses to satisfy their consumers (Shibasaki et al.2021). Moreover, international logistics contributes to the effective distribution of goods across the world, maintaining compliance with customs and regulatory requirements and reducing delays. This smooth movement of products enriches the capability of the manufacturers to tap into diverse markets thereby adding value to their international footprint (Wagener, 2017). Be that as it may, international logistics enables different manufacturing companies to maintain a delicate balance between maintaining adequate stock so that they become capable of meeting the demands of their consumers while avoiding overstocking which may tie up storage space and capital that could be utilised somewhere else (Ertem et al.2017). By dint of high-end demand planning and forecasting, the logistics experts working in the international logistics industry become capable of optimising stock levels resulting in reducing carrying expenses as well as the potential for product obsolesce which is considered to be vital during dealing with the global markets along with their diverse demands. Furthermore, by remaining in line with the global sustainability goals, international logistics helps in responsible business practices, nurturing trust and goodwill among the stakeholders (Kosuge et al.2024).
Conclusion:
Intermodal and international logistics in global manufacturing sectors are poised for potential transformation. Continuous technological advancements have been revolutionizing intermodal and international logistics and their implementation in different manufacturing sectors worldwide. Autonomous vehicles and drones have been reshaping last-mile delivery, cutting back on costs and the environmental footprint of the manufacturers in relation to their transportation and logistics operations.

